Vasopressors & Inotropes - Receptor Physiology
Introduction
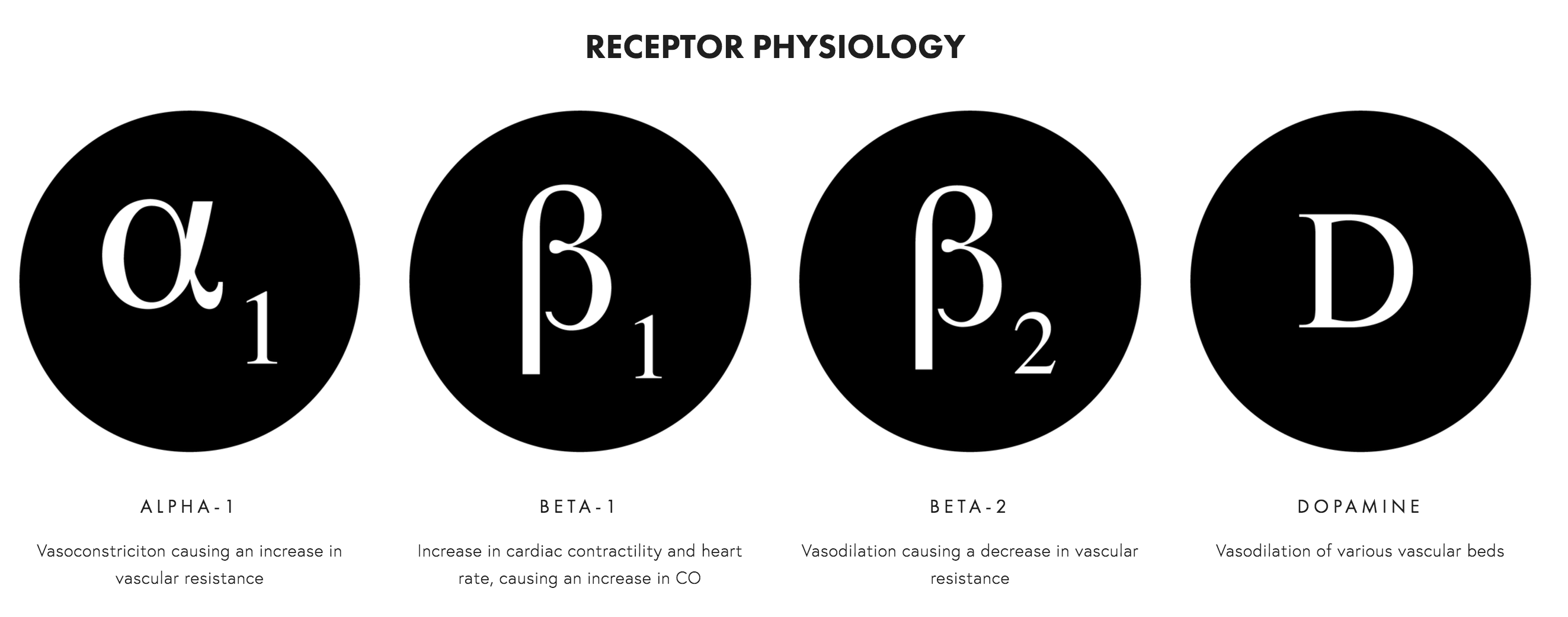
Vasopressors are a class of drugs that cause vasoconstriction and increase mean arterial pressure. Inotropes are another class of drugs which increase cardiac contractility. However it is important to note that many of these drugs have both vasopressor and inotropic effects. Vasopressors are indicated for a decrease of >30 mmHg from baseline systolic blood pressure, or a mean arterial pressure <60 mmHg when either condition results in end-organ dysfunction due to hypoperfusion. However, vasoactive and inotropic medications should never be used in place of adequate volume resuscitation or treatment of the underlying hemodynamic disorder. The main adrenergic receptors to know are the alpha-1, beta-1, and beta-2 adrenergic receptors and also the dopamine receptors. For information on specific medications, check out the article on vasopressor and inotrope medications.
Alpha-1 Receptor
Alpha-1 adrenergic receptors are found on our blood vessels, specifically smooth muscle walls. Activation of these receptors causes vasoconstriction. Alpha-1 adrenergic receptors are also found on the heart, however its clinical significance of is unclear.
Beta Receptors
Beta-1 adrenergic receptors are most common on the heart, and causes increases in inotropy and chronotropy with minimal effects on blood vessel vasoconstriction. There are also beta-2 adrenergic receptors which can be found of blood vessel smooth muscle. Stimulation of beta-2 receptors will cause blood vessel vasodilation, therefore having some effect in decreasing mean arterial pressure.
Dopamine Receptors
Dopamine receptors are present in the renal, splanchnic (mesenteric), coronary, and cerebral vascular beds. Stimulation of these receptors leads to vasodilation. There is a second subtype of dopamine receptors which causes vasoconstriction by causing norepinephrine release. Ideally, vasoactive medications should be administered through a central line. the use of a vasopressors is emergent than, peripheral administration is acceptable for short periods of time.