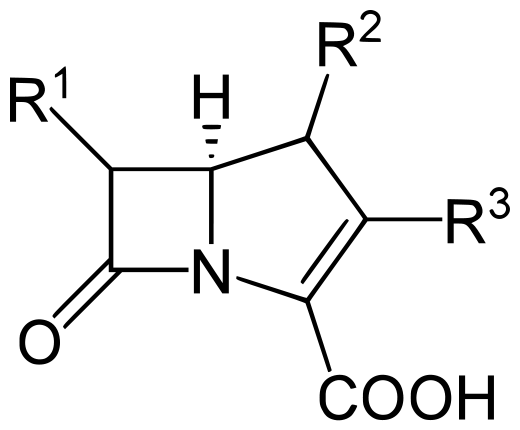
Carbapenams (Meropenem, Imipenem, Ertapenem)
Mechanism of Action
- Binds peptidoglycan binding protein to inhibit the cross-linking of peptidoglycan, therefore inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis.
- Beta-lactamase resistant
- Carbapenems are inactivated in the renal tubules by renal dihydropeptidase I.
- Cilastin is a drug often given with carbapenems, which inhibits the renal inactivation of carbapenems which increases their duration of action.
Clinical Use
Broad-spectrum
- Gram-positive cocci
- Enterococcus
- Gram-negative rods
- Enterobacter spp.
- Klebsiella spp.
- Pseudomonas spp.
- Anaerobes
*not effective against VRE or MRSA
Side Effects
- GI upset
- Allergic Reaction
- Seizures - especially with renal insufficiency, secondary to high serum levels