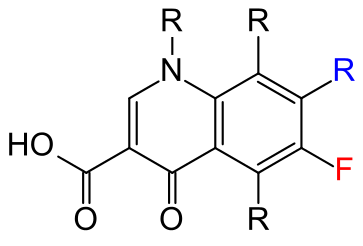
Fluoroquinolones
Mechanism of Action
A family of synthetic broad-spectrum antibiotics, fluoroquinolones inhibit the activity of DNA gyrase (topoisomerase II) by preventing bacterial DNA from unwinding and duplicating.
Clinical Use
In general the fluoroquinolones will cover common microbes causing urinary tract infections, GI infections, pneumonias and gonorrhea:
Gram-negative
- Pseudomonas
- Neisseria
- Haemophilus
- Klebsiella
- E. coli
- Legionella
Gram-positive organisms
- Enterobacter
Mycoplasma
There are "respiratory fluoroquinolones" (gatifloxacin, levoquin, moxifloxacin) that have increased activity against some gram-positive organism such as S. pneumoniae and staph species.
Side Effects
- Rash
- Tendonitis and tendon rupture
- GI upset
Contraindications
Should not be used in pregnancy since fluoroquinoles have been shown to cuase damage to growing cartilage